Good news on California’s efforts to fight climate change: in-state emissions in 2017 (the latest available data) were down over 2016 and ahead of the state’s mandatory 2020 goals. The California Air Resources Board announced the progress yesterday, with this chart showing emissions in context of population and GDP:
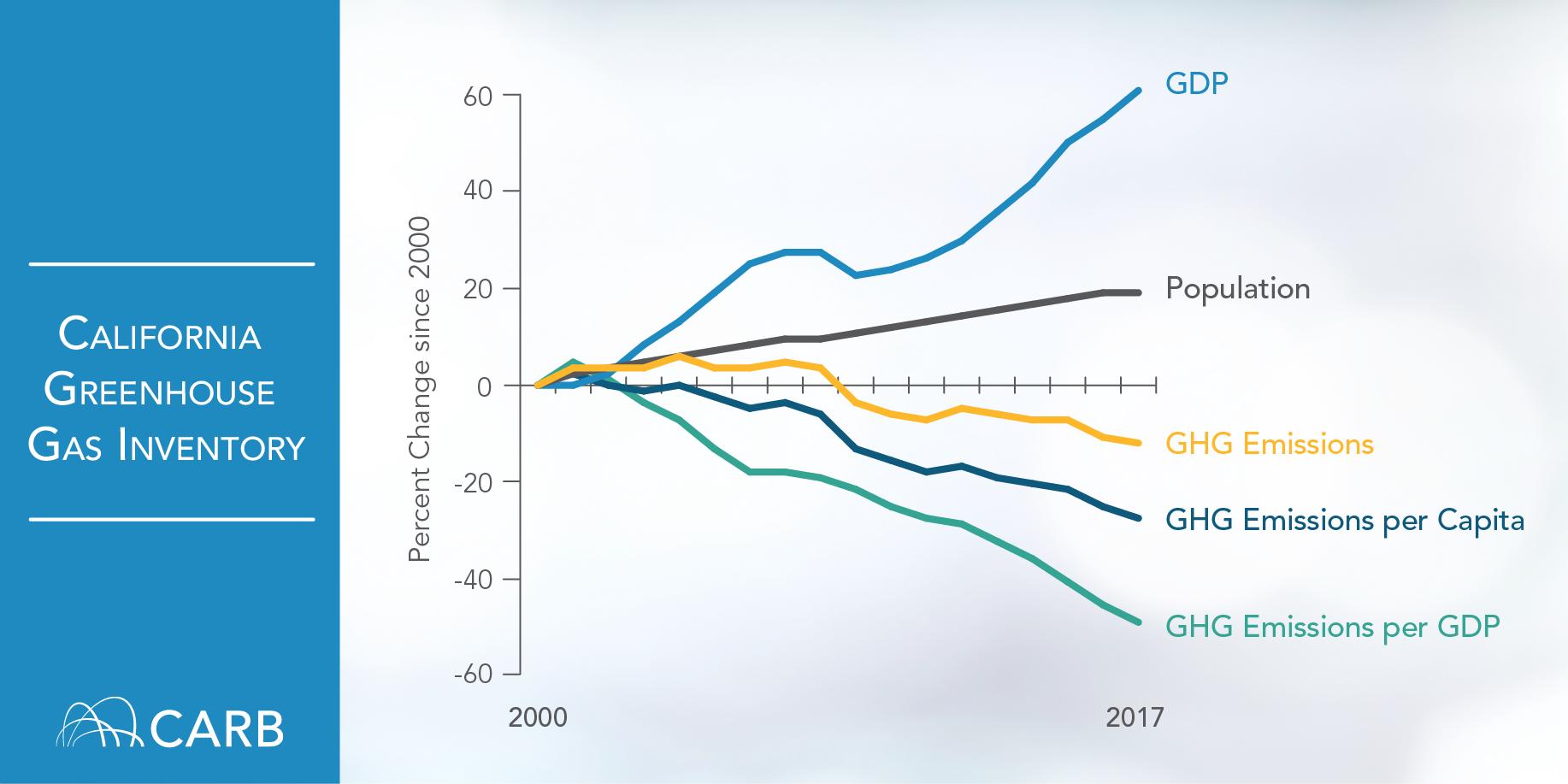
Overall, emissions totaled 424 million metric tons of carbon dioxide equivalent in 2017, down 5 million metric tons from 2016. For reference, the 2020 reduction target is 431 million metric tons.
Most of the progress came from the electricity sector, where for the first time renewable sources made up a larger percentage of the generation than fossil fuels.
However, transportation emissions increased 0.7% in 2017, compared to a 2% increase in 2016, mostly from passenger vehicles. That total is even worse when you consider pollution from oil and gas refineries that make the fuel for these passenger vehicles. Together with hydrogen production, these sources constituted one-third of the state’s total industrial pollution.
Here’s the latest pie chart on where the emissions came from in 2017:
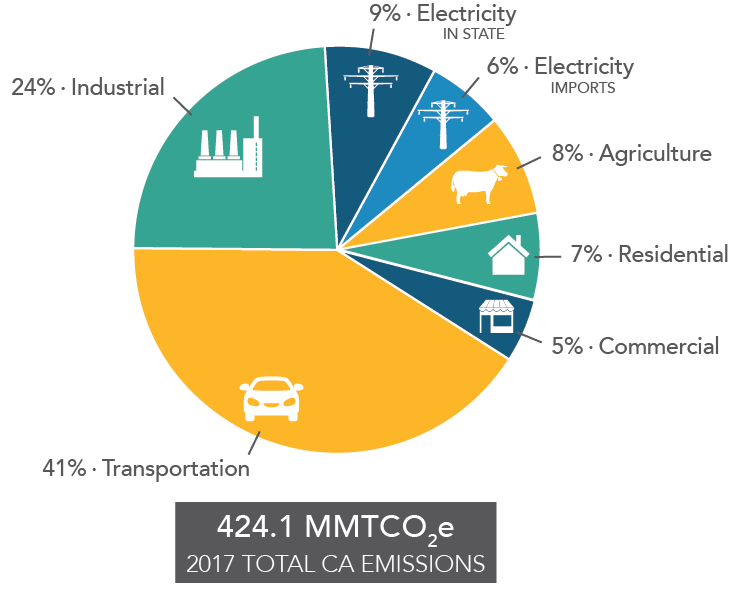
While the story is overall positive for California’s climate efforts, the state will have to redouble its efforts to reduce driving miles by allowing more homes to be built near jobs and transit, while transitioning the remaining driving miles to zero-emission technologies like electric vehicles.
California’s major urban regions are falling behind in getting people out of their solo drives in favor of walking, biking, transit and carpooling, according to a major report last month from the California Air Resources Board. In short, the state will not meet its 2030 climate goals without more progress on reducing vehicle miles traveled (VMT):
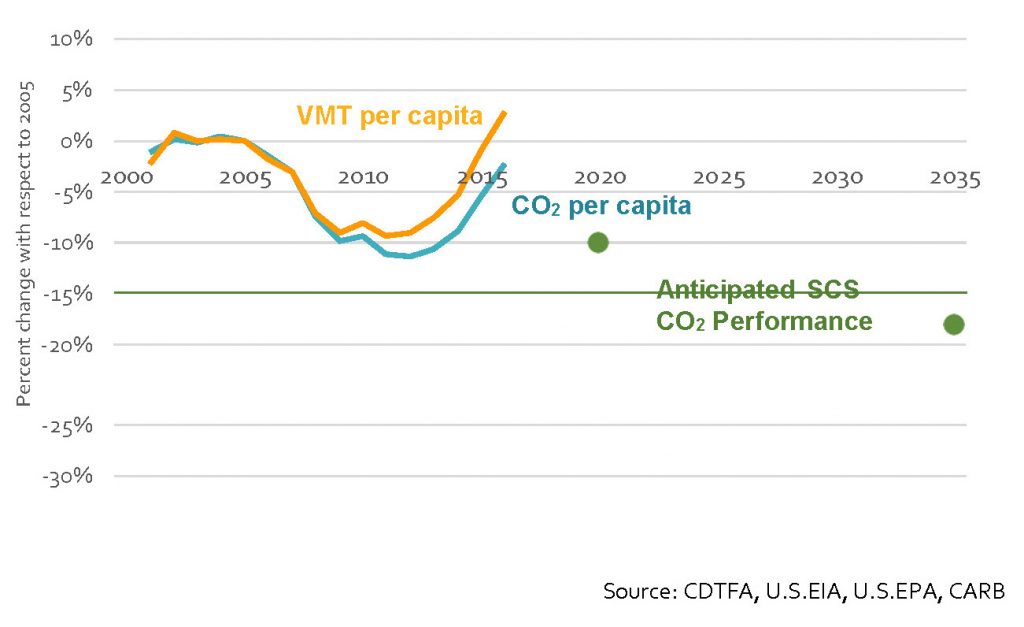 This result comes despite the decade-old passage of SB 375 (Steinberg, 2008), which promised to reorient land use and transportation around reduced driving. The lone exception appears to be the San Francisco Bay Area, which has seen steadily increasing transit ridership and decreasing solo driving to work as a percentage, according to the report.
This result comes despite the decade-old passage of SB 375 (Steinberg, 2008), which promised to reorient land use and transportation around reduced driving. The lone exception appears to be the San Francisco Bay Area, which has seen steadily increasing transit ridership and decreasing solo driving to work as a percentage, according to the report.
What are the stakes if California can’t start solving this problem in the next decade? A U.N. report on climate change recently concluded that limiting global warming to 1.5 C would “require more policies that get people out of their cars — into ride-sharing and public transportation, if not bikes and scooters — even as cars switch from fossil fuels to electrics.” In order to keep the world on track to stay within 1.5 Celsius, the report stated that emission reductions would have to “come predominantly from the transport and industry sectors” and that countries couldn’t just rely on zero-emission vehicles alone.
Yet as the report shows, California’s current land use policies are not helping with this goal. We need to discourage development in car-dependent areas while promoting growth close to jobs, as SB 50 would allow. And at the same time, we need to invest in better transit service. Otherwise, California and jurisdictions like it around the world will fail to avert the coming climate catastrophe.


