Big industry loves to demagogue the California Environmental Quality Act (CEQA), which requires environmental review for major new projects. But a new survey from the State of California shows that the law barely affects most projects where the state is the lead agency.
The study examined all state-led projects over a five-year period, from 2011 to 2016. First, 90% of the state’s projects were already exempt from the law, due to compliance with legislative or regulatory provisions that exempt certain types of projects. Second, a full-blown environmental impact report occurred less than one percent of the time, while litigation was virtually negligible. Here is the summary chart:
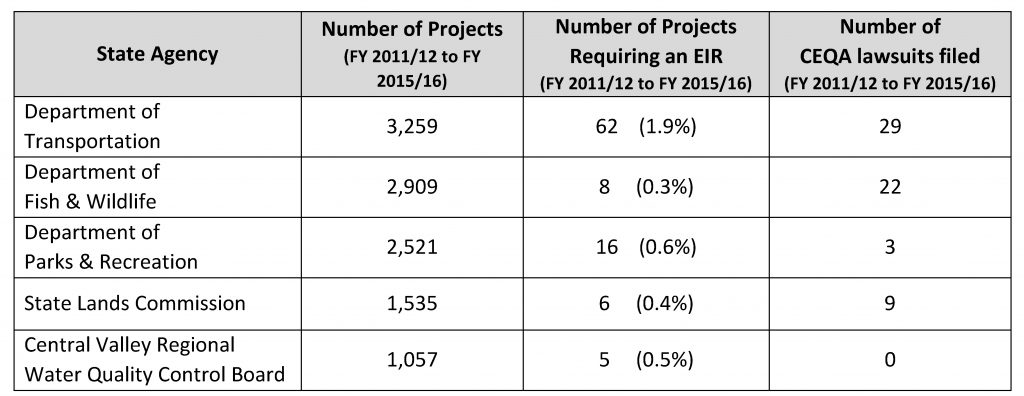 These findings are consistent with a 2016 study sponsored by the Rose Foundation, which found similarly low litigation rates (as I noted at the time):
These findings are consistent with a 2016 study sponsored by the Rose Foundation, which found similarly low litigation rates (as I noted at the time):
The number of lawsuits filed under CEQA has been surprisingly low, averaging 195 per year throughout California since 2002. Annual filings since 2002 indicate that while the number of petitions has slightly fluctuated from year to year, from 183 in 2002, to 206 in 2015, there is no pattern of overall increased litigation. In fact, litigation year to year does not trend with California’s population growth, at 12.5 percent overall during the same period.The rate of litigation compared to all projects receiving environmental review under CEQA is also very low, with lawsuits filed for fewer than 1 out of every 100 projects reviewed underCEQA that were not considered exempt. The estimated rate of litigation for all CEQA projects undergoing environmental review (excluding exemptions) was 0.7 percent for the past three years. This is consistent with earlier studies, and far lower than some press reports about individual projects may imply.
So while big polluters and sprawl developers and their law firm allies have gone to great lengths to demonize the law and the rare litigation that results, the facts just aren’t matching.
It’s still true that CEQA can be a barrier to new development. But based on the data so far, it’s just not a major one.


